Fiber optic splice closures are protective housings that are used to protect and organize spliced fiber optic cables. These closures are an essential component of any fiber optic network, as they provide a secure and weather-resistant environment for the spliced fibers, ensuring their continued proper functioning.
Fiber optic cables are made of incredibly thin strands of glass or plastic that are used to transmit data over long distances. These cables are incredibly sensitive to physical damage, and even a small crack or kink in a fiber can cause the data transmitted through it to be lost or corrupted. Splice closures protect the spliced fibers by encasing them in a protective housing that shields them from physical damage, as well as environmental factors such as water and dust.
One of the main benefits of fiber optic splice closures is their ability to provide a high level of protection against water and moisture. These closures are sealed against the elements, ensuring that water and moisture cannot penetrate the housing and damage the spliced fibers inside. This protection is essential in areas where the cable may be exposed to water, such as underground or in overhead applications.
Another key feature of fiber optic splice closures is their ability to organize and manage the spliced fibers. These closures typically have a series of trays or guides that are used to keep the fibers in a neat and orderly configuration. This helps to prevent fibers from getting tangled or kinked, which can cause damage or signal loss.
Additionally, fiber optic splice closures are designed to be easy to install and access, allowing for easy maintenance and troubleshooting. They come in different sizes and shapes depending on the different application, such as aerial, underground, direct buried, and indoor or outdoor. This makes it simple for technicians to access the spliced fibers for maintenance or repair.
Types of fiber optic splice closures:Dome (Vertical) Fiber Splice Closures and Horizontal Fiber Splice Closures
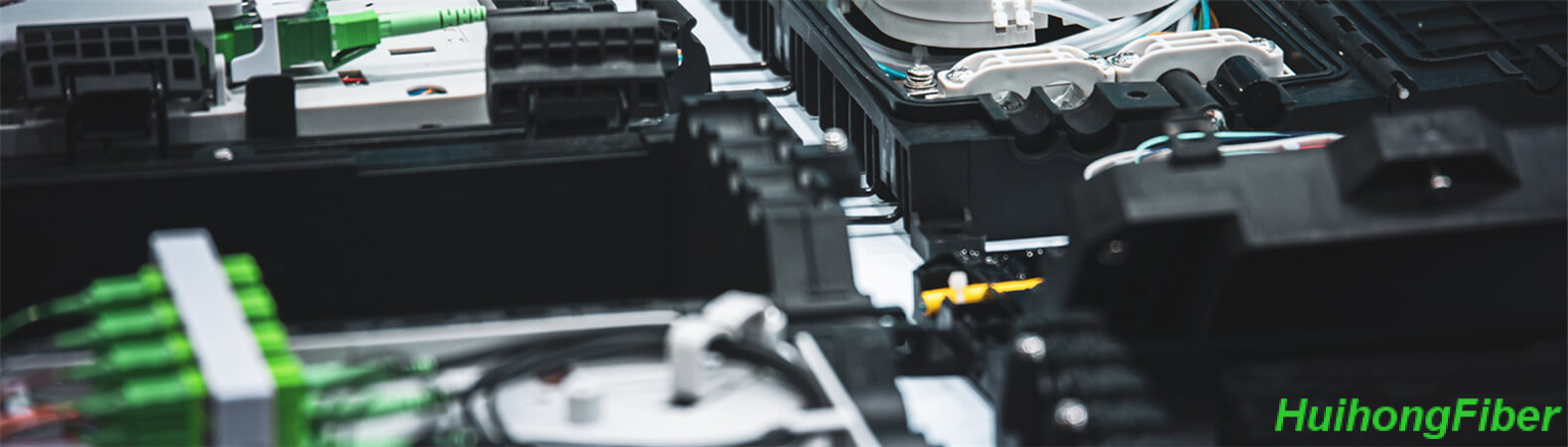

Fiber optic splice closures are used to protect and organize fiber optic splices, which are the points where two fibers are joined together. There are two main types of fiber optic splice closures: dome (vertical) fiber splice closures and horizontal fiber splice closures.
Vertical fiber optic closures, also known as dome fiber optic splice closures or fiber dome closures, are designed to resemble a dome shape. This allows them to easily be buried in a variety of applications, but they can also be used above ground. There is a wide range of models and configurations available to meet the increasing demands of modern fiber optic networks, including high-capacity versions and various numbers of splicing trays. The number of inlet/outlet ports on the dome fiber optic closure may also vary depending on the specific needs of the application. These closures require high-level seals and waterproof technology due to their potential underground use, and it is important to keep insects and dirt out to ensure proper functioning in such environments.
Horizontal fiber optic splice closures are a vital component in any fiber optic network. These closures are designed to protect and secure fiber optic splices from external elements such as water and dust. They are typically made of high tensile construction plastic, which gives them good adaptability and compression resistance. These qualities make them suitable for use in a variety of environments and conditions. However, it is important to ensure that these closures are firmly attached to a pole or wiring, as they can be prone to damage from weather and wind if not properly secured. By using horizontal fiber optic splice closures, you can ensure the long-term reliability and performance of your fiber optic network.
Both types of fiber optic splice closures are designed to protect the splices from damage and to keep them organized for easy maintenance. They are an essential component of any fiber optic network and are used in a wide range of applications, including telecommunications, internet service providers, and cable television.
Factors to consider when selecting fiber optic splice closures

Fiber optic splice closures are an important component in the installation and maintenance of fiber optic networks. They provide protection for the spliced fibers and help to organize and manage the fibers within the closure. When selecting a fiber optic splice closure, there are several factors that should be considered to ensure that the closure is appropriate for the specific application and meets the needs of the network.
Type of closure: There are several different types of fiber optic splice closures available, including indoor, outdoor, underground, and aerial closures. The type of closure needed will depend on the specific application and whether the closure will be used in a protected or harsh environment.
Capacity: The capacity of the closure is an important consideration, as it will determine how many fibers can be spliced within the closure. The capacity should be chosen based on the number of fibers that need to be spliced and the space available for the closure.
Splicing method: Fiber optic splice closures can use different splicing methods, including mechanical splicing and fusion splicing. The choice of splicing method will depend on the specific application and the preference of the installer. Mechanical splicing is typically faster and easier to perform, but fusion splicing is more reliable and has lower insertion loss.
Accessibility: It’s important to consider accessibility when selecting fiber optic splice closures. The closure should be designed to make it easy to install and maintain the fibers within the closure, including the ability to access and change the fibers when necessary.
Durability: The durability of the closure is important to ensure that it can withstand the harsh conditions of the installation environment. The closure should be constructed of high-quality materials that are resistant to corrosion, impact, and extreme temperatures.
Quality and reliability: Quality and reliability are crucial when selecting a fiber optic splice closure. The closure should be manufactured to the highest standards and be designed to withstand the stresses of the installation environment. It’s also important to ensure that the closure is designed to provide long-term protection for the spliced fibers.
Selecting the right fiber optic splice closure requires careful consideration of a variety of factors. By taking into account the type of closure, capacity, splicing method, accessibility, durability and quality, you can ensure that the closure is suitable for the specific application and will provide long-term protection for the spliced fibers.
Installation and maintenance of fiber optic splice closures
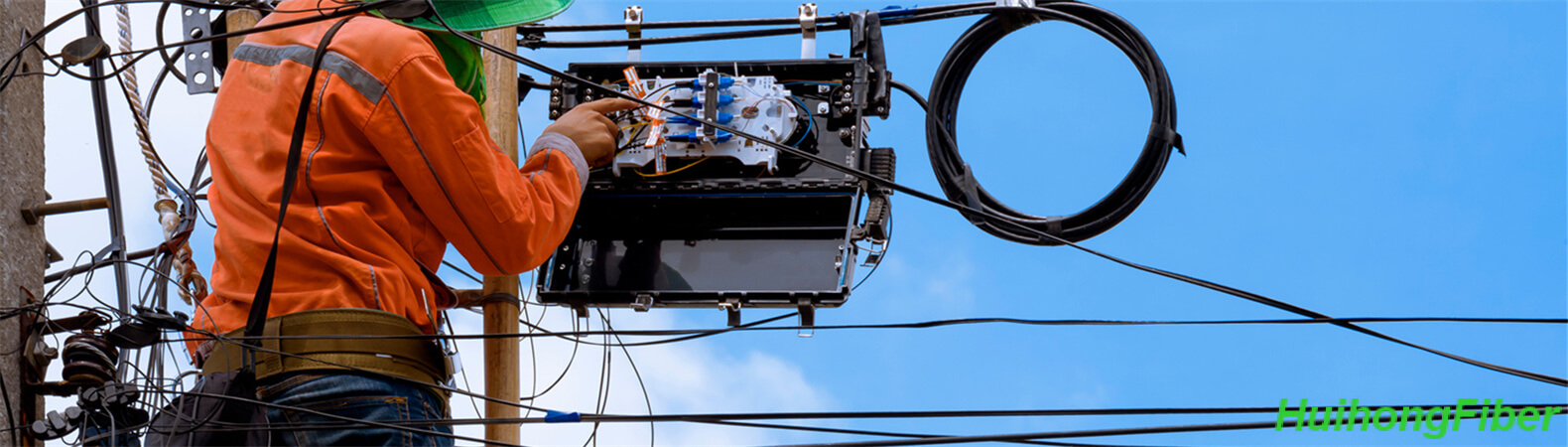
1.Optical Fiber Preparation
In the process of installing a fiber splice closure, the preparation of the optical fiber begins by removing the outer cover of the cable (if present) including the shield and armor. Next, successive layers are stripped to expose the loose tube. It is crucial to follow the guidelines provided by the cable’s manufacturer. It’s important to note that the recommended length for preparation is 3 meters. The loose tube should then be cleaned and the core-sheath should be reinforced using detergent. Any excess filler tube should be removed, and the outer cover of the fiber optic cable should be smoothed with the provided sandpaper.
2.Optic Fiber Installation
To install optic fiber in a fiber splice closure:
1.Choose a sealing ring with the smallest diameter that fits the outer diameter of the fiber optic cable, and place it on the cable.
2.Insert the fiber optic cable into the designated entry hole.
3.Attach the cable shield and ground.
4.Secure the sealing rings with self-adhesive sealing tape, ensuring the tape is flush with the outside diameter of the rings to form a sealed end on the fiber optic cable.
5.Insert the sealed end of the cable into the hole for the optical cable.
6.Secure the holder and cable core support using a hose clamp, and fix the cable in the connector box base, then tighten the hose clamp screws.
7.Tie nylon ties and trim any excess.
8.Seal the unused portion of the fiber optic cable with a plug, and wrap it with sealing tape.
9.Apply reinforcing materials to the countersunk screw of the fusion tray support, and press it tightly.
3 fiber optic splicing:
To perform fiber optic splicing in a splice closure, first prepare the fiber by coiling 1.5 turns on the tray, then coil all remaining fibers in the box. For single-core fiber, use a single-core buffer tube on the tray, and for ribbon fiber, use a ribbon buffer tube. Secure the inlet of the fusion splice tray with a nylon tie. Carefully connect the two fibers using the specified method, place the splice in the fusion unit slot, and coil any remaining fiber in the tray. Cover the fusion splice tray and secure it in place. The number of stacked trays will depend on the capacity of the splice box required. When stacking multiple trays, ensure they meet inspection and maintenance requirements for fiber optic splicing. To stack two trays, use the three buttons on each tray, and for five trays use the same method. If you need to check the condition of a specific tray, simply remove it from the top layer.
4.Sealing Instruction
Instructions for Sealing Fiber Optic Fusion Closures:
1.Tighten the valve nozzle with the ground screw before sealing.
2.Insert the sealing strip into the sealing slot and the “U” shaped slots at both ends of the splice closure. Avoid pulling the sealing strip artificially to prevent leakage.
3.Carefully close the top cover of the splice enclosure and fasten it using the bolts in the order indicated on the cover. Do not use a torque wrench to exceed 25N-m.
4.After 5 minutes, re-tighten the bolts in the same order using a torque wrench, ensuring the torque still does not exceed 25N-m.
Common issues and troubleshooting techniques for fiber optic splice closures
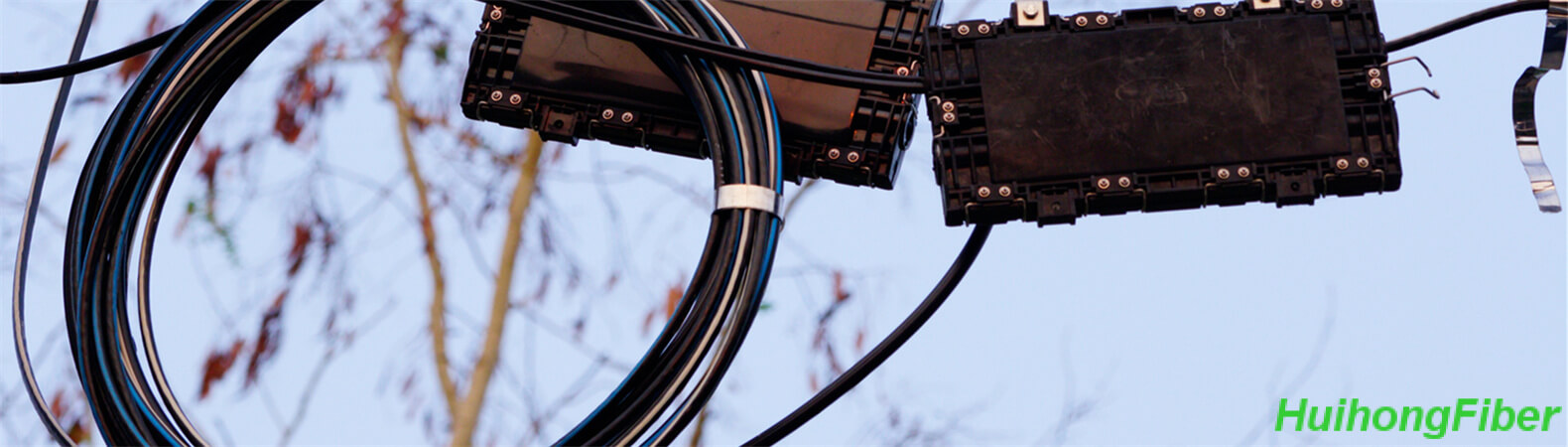

One common issue with fiber optic splice closures is damage to the spliced fibers. This can happen during installation or as a result of external factors such as weather or physical impact. To troubleshoot this issue, it is important to first inspect the closure for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or broken parts. If damage is found, the affected fibers will need to be respliced and the closure will need to be repaired or replaced.
Another issue that can occur with fiber optic splice closures is water ingress. This can happen as a result of a poor seal on the closure or damage to the closure itself. To troubleshoot this issue, it is important to inspect the closure for any signs of water damage, such as rust or mold. If water ingress is found, the closure will need to be resealed or replaced to prevent further damage to the spliced fibers.
A third issue that can occur with fiber optic splice closures is improper fiber routing. This can happen if the fibers are not properly routed through the closure during installation. To troubleshoot this issue, it is important to inspect the closure and make sure that the fibers are properly routed through the designated pathways. If the fibers are not properly routed, they will need to be rerouted and the closure will need to be resealed to protect the spliced fibers.
Lastly, another common issue is connector or fiber cleaning and maintenance, if debris or dust accumulates on connector end-faces or on the fibers it can cause high attenuation, connector loss and even connector damage, to troubleshoot this issue it’s important to use the appropriate cleaning tools and methods like dry cleaning or wet cleaning, such as lint-free wipes, fiber cleaning pens, or alcohol cleaning solution for the connectors and fibers.
Fiber optic splice closures play an important role in protecting and organizing spliced fiber optic cables. However, they can experience issues such as damage, water ingress, improper fiber routing, or connector maintenance issues. By being aware of these common issues and using the troubleshooting techniques discussed above, you can quickly and effectively resolve any problems that may occur with your fiber optic splice closures.
More tips to use the fiber optic splice closures
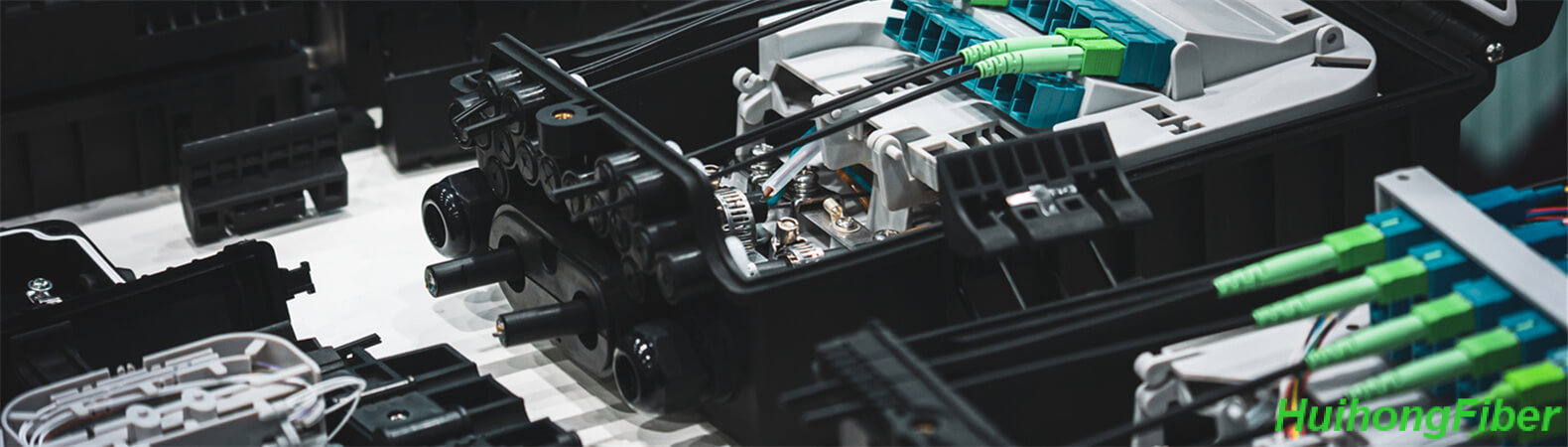
The quality and lifespan of a fiber optic project relies heavily on the preparation of the fiber end face. A smooth, defect-free, and burr-free end face allows for successful splicing with a fusion splicer, resulting in a joint that meets project requirements. However, if the end face is not properly prepared, the fusion splicer may not function properly, or the joint may not meet engineering standards. To ensure a proper end face, it’s crucial to strip the coating of the fiber perpendicular to the fiber axis, to avoid scratches. The fiber should also be cut with precision and care, using a specialized cutter that makes a clean, fast break, rather than crushing the fiber. The fiber should be handled with care to prevent any damage or bruising to the end face. The fusion splicing machine, which is highly precise and costly, should be operated strictly in accordance with instructions to avoid loss or damage. Additionally, operators should pay special attention to the operating procedures of the welding machine and ensure that the length of the heat shrink tube meets the required specifications.
After completing the fiber optic fusion splicing, it’s important to protect the fiber by using a heat-shrinkable tube and wrapping any remaining fiber. In the process of winding the fiber, ensure that the bending radius is not too small, typically no less than 4mm. If the radius is too small, it can cause significant refractive loss and increased dispersion, and over time, may result in fiber breakage. When winding, pay attention to the direction of the fiber’s twist, which is usually in the shape of an inverted “8”. Carefully handle the fiber to avoid breaking it. Once the winding is finished, place all fibers under the tray’s protective barrier to prevent damage during packaging.
When stripping fiber optic cable, it is important to be mindful of the depth of feed. To properly remove the outer sheath of the cable, it is crucial to have a good understanding of the sheath cutting depth. A technique to achieve this is to rotate the sheath cutter while observing the cut. If the white polyester tape becomes visible, you should stop feeding and remove the cutter. It may take some practice to master this technique. After stripping the outer sheath, fix the cable to the fiber optic splice closure and strip the core bundle tube. To ensure a successful fiber optic splicing, pay attention to the following three key points:
The core bundle tube should not be twisted, and the filler tube must be beneath the rebar, not the fiber bundle. Before fixing the cable, ensure that the position of the fiber bundle tube is aligned with the rebar. If the rebar is pressed on the core bundle tube, it can cause excessive loss and potential breakage of the fibers.
The length of the rebar should be appropriate. After determining the position of the core bundle tube, fix the fiber optic cable in place to avoid any loose fibers. Be mindful of the length of the reinforcement; if it is too long, it won’t fit in the splice closure, and if it is too short, it won’t secure the cable properly. The distance between the clamp plate and the screw that fixes the reinforcement should be equal to the remaining length, and the rest of the cable should be fixed after the reinforcement.
The stripping length of the core bundle tube should be appropriate. After fixing the cable, the core bundle tube can be opened. A stripping length that is too long can damage the rest of the fiber when winding it, while a stripping length that is too short can damage the fiber by causing the fixing clip to get stuck on it. It is generally recommended to strip through two fixed clips, as this length will not cause damage to the fiber and will fix it securely. However, when fixing, the clips should not be too tight, as this can cause the fibers to be lost under stress and break over time, which could present a safety hazard.
The proper sealing of a splice closure is crucial in the project. A wet splice closure can easily cause damage to the fibers inside, leading to breakage over time. Careful sealing is necessary, especially when the closure is buried underground. The main area of sealing for a splice box is between the upper and lower covers of the fiber optic cable and the splice closure itself. To ensure proper sealing, the cable sheath should first be polished and the outer sheath should be smoothed with gauze, allowing for a tight fit between the cable and sealing tape. The seal between the upper and lower covers of the splice closure should be designed to ensure even distribution of sealing tape into the sealing slot and secure tightening of screws.
